
Rove beetle, An insect do you know it
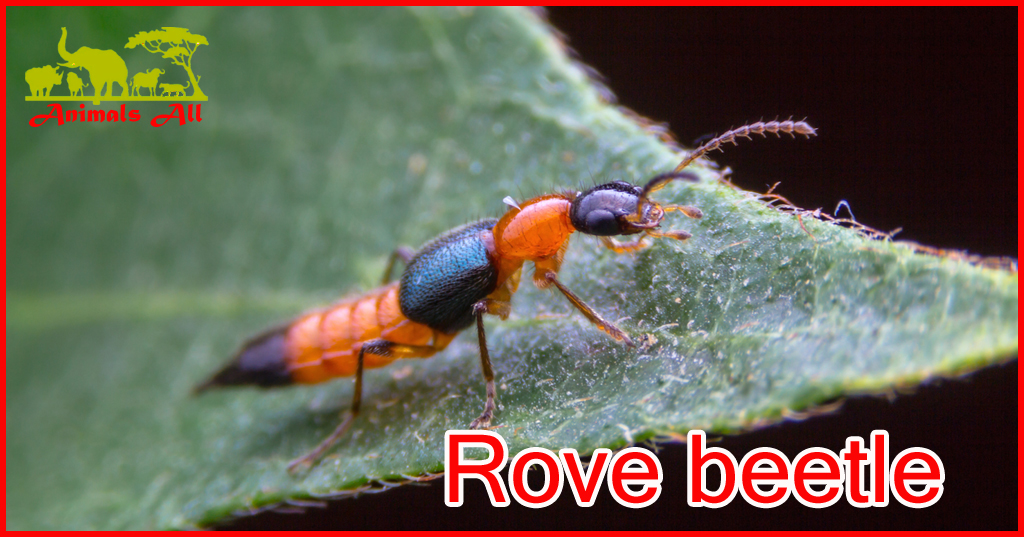
Rove beetle, also known as “shadow beetles” and “green waist beetles”, are the common name for beetles in the family Rovetidae of the order Coleoptera. They belong to the class Insecta, order Coleoptera, and family Rovetidae . They are the family with the richest species in the order Coleoptera. The elytra are very short, and most species in this family get their name because their hind wings are hidden under their front wings and are not easily noticed. Among them, poisonous rove beetles are threatening to humans because of the venom in their bodies. But they are not fatal.
Rove beetles are divided into 14 subfamilies, more than 900 genera, and more than 20,000 species, which are widely distributed all over the world. They look like termites, with a body length of about 0.5~1.0 cm, an orange-yellow body, and a dark blue head, thorax, and tail, so they are commonly known as “green ants”. Rove beetles like to live in paddy fields, grasslands, and woods. They have a habit of phototropism and often fly into places with lights at night to eat decaying plants and rotten animals. Rove beetles do not sting people. Rove beetle dermatitis occurs when people come into contact with the body fluids of rove beetles, which contain the irritant “pederin”. After 10~15 seconds of contact, they react and feel severe burning pain, causing blistering and ulceration of the skin. This is rove beetle dermatitis.
Rove beetle is a common name for beetles in the family Rove beetle of the order Coleoptera . It belongs to the large class of rove beetles (Staphyli niformia) of the suborder Polyphaga, and is the most species-rich family in the order Coleoptera. The elytra are extremely short, and are named because they are hidden under the forewings and are not easily noticed .
Origin of the name

Rove beetles are divided into 14 subfamilies and more than 900 genera, with more than 20,000 species, and are widely distributed around the world. They look like termites, with a body length of about 0.5 to 1.0 cm, an orange- yellow , and a dark blue head, thorax, and tail, so they are commonly known as “green ants.” Rove beetles like to live in paddy fields, grasslands, and woods. They have a habit of being phototropic and often fly into places with lights at night to eat decaying plants and rotten animals.
Rove beetles do not sting people. Rove beetle dermatitis occurs when people come into contact with the body fluids of rove beetles , which contain the irritant “pederin”. After 10 to 15 seconds of contact, they react and feel severe burning pain, causing blistering and ulceration of the skin. This is rove beetle dermatitis . It has been found that 1-2 drops of Fengyoujing be mixed with about 500ML of clean water, applied to the body before going to bed, or sprayed on the gathering place, which has a miraculous effect.
Physical characteristics
An insect of the family Staph ylinid, order Coleopterous , including more than 3,200 genera and about 46,200 species worldwide. The number of species is increasing at a rate of 300-400 per year. They are often found around decaying plants and animals and feed on carrion. Most are slender and small, usually less than 3 mm (or 1/8 inch) long, and the largest does not exceed 2.5 cm (1 inch). The elytra are short and thick, and the hind wings are well developed. They can be quickly unfolded from under the elytra when taking off.
After flying, they are folded up with the help of the abdomen and legs and hidden under the elytra again. When frightened, they raise the end of their abdomen and shoot a foul-smelling mist at the enemy . The larvae are wingless and look like adults. Some large species have beautiful black and yellow colors, like wasps; some look and behave like soldier ants . The genera Lomechusa and Atemeles in Europe and Xenodusa in North America live in ant or termite nests . They secrete a liquid for the ants to eat, and the ants feed them in return.
Living habits
The poisonous rove beetle , also known as the ” green waist insect “, is 0.6 to 0.8 cm long and is similar to a flying ant . When it stops, its tail twists up and down and retracts its wings. The phototactic and lives under weeds and rocks during the day and comes out at night. It is most common in summer and autumn and likes to fly around fluorescent lights. It has no venom glands on the outside and will not sting people, but it has venom in its body (strong acidic venom, pH 1 to 2), which will flow out after being killed. The venom of the rove beetle can cause acute skin inflammation, and the color of the wound will be different from the surrounding skin after healing.
The development of the poisonous rove beetle is complete metamorphosis. The life cycle has four stages: egg, larva (two instars), pupa and adult. It breeds mostly in hidden and humid environments. The larvae and adults are predators, preying on pests in rice fields . Adults often live in humid environments. Some species often fly indoors when attracted by lights on hot and humid nights . The number of generations each year varies from one to several generations depending on the region . It overwinters as an adult.
Distribution Environment
Rove beetles mostly breed in hidden and humid environments. Such as freshwater lakes , ditches, ponds, river floodplains, weeds, and rice, corn and other crop fields. Rove beetles are active during the day, often crawling on the stems and leaves of crops or weeds, and run very fast when frightened. They feed on small insects, plant pollen , and rotten organic matter. They have obvious phototropism (especially for fluorescence ). The stronger the light, the more insects are attract. They are also alotropistic.
Under the same conditions , rove beetles always like to fly to high places. They crawl very fast. After flying into the room, they crawl around on the ceiling, walls, furniture, clothing surfaces , and human bodies, making people sick. Rove beetles that enter the room can withstand hunger for several days, causing continuous damage to the human body. The frequency of rove beetle’s nighttime activities is affect by many factors such as temperature, wind direction, and light.
Bite damage
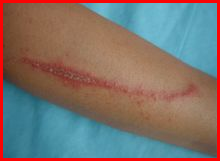
When human skin comes into contact with a small amount of venom (such as when a rove beetle crawls over the skin). The skin will develop red spots, flakes, or stripes , followed by gray-brown necrosis in the center . If the injured area is not large, there will be a slight itching and pain. If the injured area is large (such as when a rove beetle crawls over multiple parts of the skin). There will be a strong itching and pain sensation, which may be accompanied by swollen lymph nodes , fever, etc.
If human skin comes into contact with a large amount of venom (such as venom flowing onto the skin), blisters will form at the injured part. The surrounding skin will become red and swollen. There will be a circle of the original skin color between the blisters and the redness and swelling. The blisters can be break, such as by squeezing them with a cotton swab and then washing them with salt water. But blisters will form again soon. After the blisters disappear naturally soon.
The affected part will bulge, and the original blister in the middle will be sunken. Like a crater, but generally craters are round, while the affected part on the skin is linear . The skin tissue at the raised part of the affected part will all be necrotic, forming a dark brown scar. New skin will grow under the scar , but the color of the new skin is very light. Which is somewhat different from the surrounding skin, resulting in the affected part looking like a cut after healing after healing . Therefore, the scar left behind has the greatest impact on the skin.
Skin Damage
As for whether the skin will be damage after the rove beetle crawls over it, some people think it will not, because the beetle is not kill and the venom does not leak out; some people think it will, because the needle-like structure on the tail of the beetle will touch the skin. In fact, it will (personal experience ), but the consequences are only slight itching and peeling.
After being crawled by a rove beetle, be sure to keep the affected area clean. It will generally heal on its own. However, in order to speed up the healing process, prevent skin infection. Reduce the itching and pain. The patient should immediately go to the dermatology department of an authoritative hospital for medical treatment. Generally, the doctor will prescribe external medication to apply to the affected area. It will heal in about two weeks.
Prevention
Maintain indoor and outdoor hygiene , prevent mosquito breeding , and close the screen windows.
2. Turn off the lights before going to bed and check if there are any rove bugs on the bed before going to bed .
3. Try to take various mosquito repellent measures, such as using mosquito repellent devices, applying floral water, etc.
4. If a rove beetle stays on your skin, do not slap it directly with your hands . Use your mouth to blow it away.
5. When going out to play, take necessary precautions and try to wear long-sleeved clothes.


One thought on “Rove beetle, An insect do you know it”
Comments are closed.